A quick guide on how to migrate your Debian 13 (Trixie) system from NVIDIA to AMD GPU.
⚠️ Disclaimer:
Use this guide at your own risk.
Make sure to back up your system first!
(Personally, I use Rescuezilla to generate a whole snapshot of my drive.)
0. How did I end up here?
Approximately one year ago I made a post on how to install NVIDIA drivers on Debian 12. Seems a bit odd that I’m showing you how to switch from NVIDIA to AMD now. To clarify things first – I was totally satisfied with my setup after setting up the proprietary NVIDIA drivers properly. Occasional gaming was working, as well as some local LLM inference.
However, I recently got the chance to buy an used AMD GPU at a very fair price from a friend of mine. I was tempted to see the performance increase from 6GB to 16GB VRAM for my local LLM inference. Besides that, I have heard that AMD GPUs are just a bit better suited for gaming on Linux. It sounds a bit like I’m selling this upgrade to myself, but it was really a performance jump worth investing in.
1. Preparation – Boot with the AMD GPU
The good thing is that Debian already comes with some AMD drivers installed. To start the migration you just need to swap the GPUs – the rest will be done after the first boot.
2. Remove all NVIDIA packages
To start off, we will remove all NVIDIA packages and related configuration files:
sudo apt purge '^nvidia.*'
After this, we want to clean up orphan dependencies with:
💡 Pro Tip: use the
--dry-runflag to first check what would be auto-removed.
sudo apt autoremove --purge
Verify that no NVIDIA package is left:
dpkg -l | grep -i nvidia
You will probably still see some packages listed. However, we need to differentiate now depending on the status code of the package:
ii– package installedrc– package removed, but config file still remaining
Ideally, you should only see the rc status codes.
To finally remove the remaining config files run:
sudo dpkg -P $(dpkg -l | awk '/^rc/ && /nvidia/ {print $2}')
3. Remove NVIDIA Xorg configuration (mandatory if nvidia-xconfig was used before)
sudo rm -f /etc/X11/xorg.conf
sudo rm -rf /etc/X11/xorg.conf.d/10-nvidia.conf
These files are often created by nvidia-xconfig and can block the AMD driver.
4. Remove Nouveau blacklist (if present)
grep -R nouveau /etc/modprobe.d/
If you find a file such as nvidia-blacklists-nouveau.conf, delete it:
sudo rm /etc/modprobe.d/nvidia-blacklists-nouveau.conf
5. Install AMD firmware and drivers
Ensure non‑free‑firmware is enabled in /etc/apt/sources.list.d/YOUR_EXISTING_FILENAME.sources:
Types: deb
URIs: http://deb.debian.org/debian/
Suites: trixie
Components: main non-free-firmware non-free contrib
Signed-By: /usr/share/keyrings/debian-archive-keyring.gpg
Types: deb
URIs: http://deb.debian.org/debian/
Suites: trixie-updates
Components: main non-free-firmware non-free contrib
Signed-By: /usr/share/keyrings/debian-archive-keyring.gpg
(This should already be the case, since proprietary NVIDIA drivers were installed before.)
Then install the required packages:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install \
firmware-amd-graphics \
xserver-xorg-video-amdgpu \
mesa-vulkan-drivers \
mesa-va-drivers \
mesa-vdpau-drivers \
libgl1-mesa-dri \
vulkan-tools
For some 32‑bit applications (Steam, Wine) it might be useful to also have 32‑bit drivers:
sudo dpkg --add-architecture i386
sudo apt update
sudo apt install mesa-vulkan-drivers:i386 libgl1-mesa-dri:i386
6. Regenerate initramfs
sudo update-initramfs -u -k all
This guarantees that no NVIDIA modules are loaded at boot.
7. Reboot
sudo reboot
8. Verify the transition
After reboot:
Kernel driver
lspci -k | grep -EA3 'VGA|Display'
You should see something like this:
daniel@DESKTOP ~> lspci -k | grep -EA3 'VGA|Display'
2d:00.0 VGA compatible controller: Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. [AMD/ATI] Navi 21 [Radeon RX 6800/6800 XT / 6900 XT] (rev c0)
Subsystem: Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. [AMD/ATI] Radeon RX 6900 XT
Kernel driver in use: amdgpu
Kernel modules: amdgpu
OpenGL
glxinfo | grep "OpenGL renderer"
Expect output similar to:
daniel@DESKTOP ~> glxinfo | grep "OpenGL renderer"
OpenGL renderer string: AMD Radeon RX 6900 XT (radeonsi, navi21, LLVM 19.1.7, DRM 3.61, 6.12.57+deb13-amd64)
Vulkan
vulkaninfo | grep driverName
In my example:
daniel@DESKTOP ~> vulkaninfo | grep driverName
driverName = radv
driverName = llvmpipe
9. Additional packages you might want to install:
rocm-smi
sudo apt install rocm-smi
Will give you a performance monitor:
daniel@DESKTOP ~> rocm-smi
========================================= ROCm System Management Interface =========================================
=================================================== Concise Info ===================================================
Device Node IDs Temp Power Partitions SCLK MCLK Fan Perf PwrCap VRAM% GPU%
(DID, GUID) (Edge) (Avg) (Mem, Compute, ID)
====================================================================================================================
0 1 0x73bf, 54752 46.0°C 10.0W N/A, N/A, 0 500Mhz 96Mhz 0% manual 229.0W 95% 10%
====================================================================================================================
=============================================== End of ROCm SMI Log ================================================
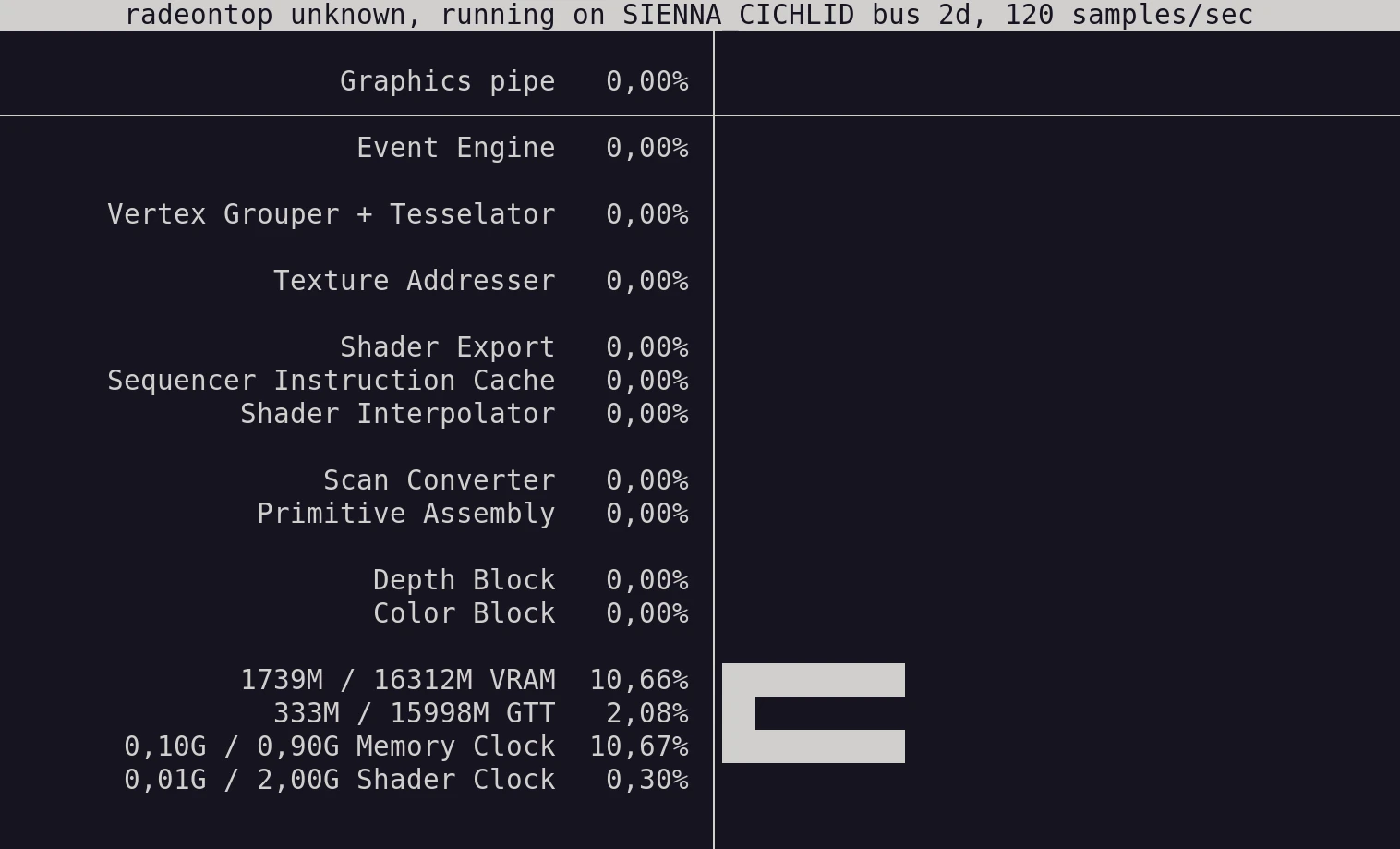
radeontop
sudo apt install radeontop
Will give you another performance monitor: